
Newton’s first law:An object continues in motion with constant speed in a straight line (constant velocity) or stays at rest unless acted upon by a net external force.
IB PHYSICS DATA BOOKLET FREE
Fnet(resultant force)is the vector sum of all forces acting on an object Free Body Diagramis a sketch of a body and all forces acting on it.

W = mg Force is an influence on an object that causes the object to accelerate
Inertia is resistance an object has to a change of velocity Mass is numerical measure of the inertia of a body (kg) Weight is the gravitational force acting on an object. ▪ This is called theterminal velocity/speed. ▪ The drag force increases as the speed of the falling object increases resulting in decreasing downward acceleration ▪ When the drag force reaches the magnitude of the gravitational force, the falling object will stop accelerating and fall at a constant velocity. Average Acceleration: slope of the straight line joining the initial andfinal position on the velocity - time graph (Instantaneous) acceleration at a given point: slope of the tangent line at given time on the velocity - time graphĭisplacementis the area under velocity– time graph Change in velocity is the area under acceleration– time graphĪir resistance provides adrag force to objects in free fall. (Instantaneous) velocityat a given point: slope of the tangent line at given time on the position -time graph.

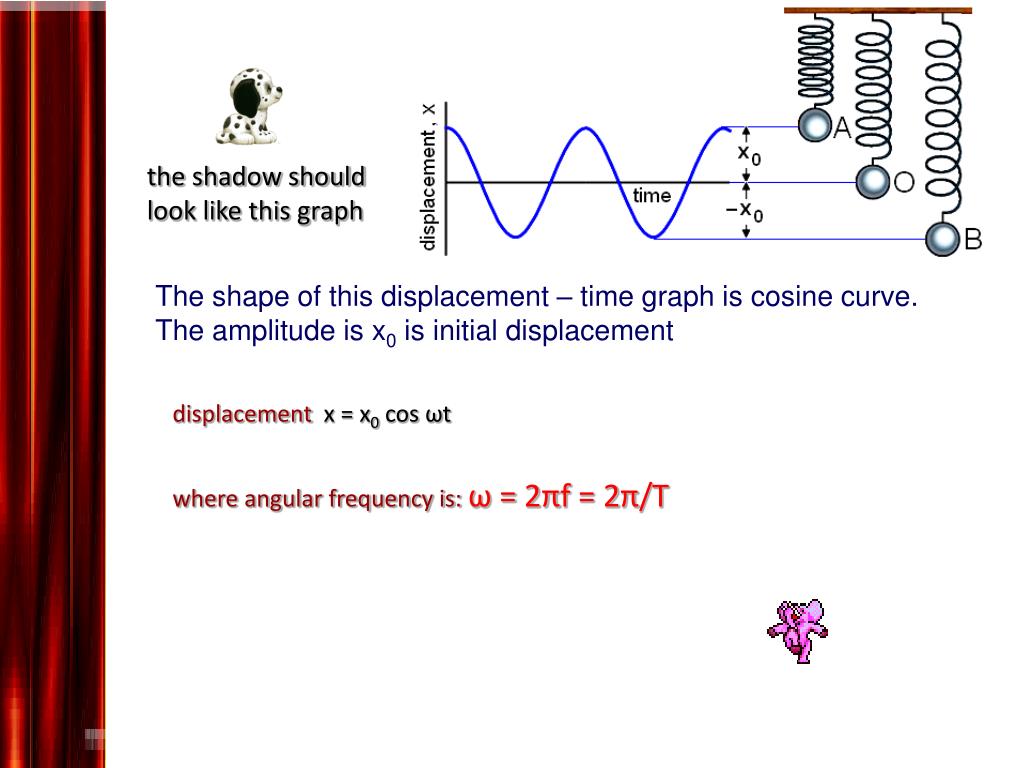
Graphs: Average velocity: slope of the straight line joining the initial andfinal position on the position -time graph.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
